
 |
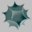
| Figure 1: A 4-dimensional realization. |
 |
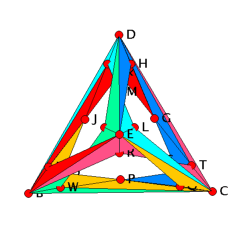
| Figure 2: The linked link of vertex A. |
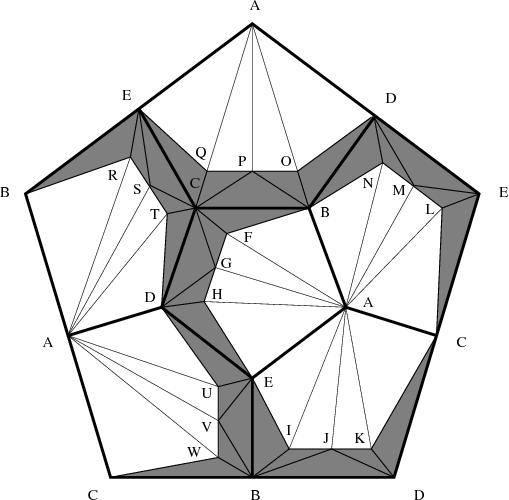 |
| Figure 3: A Z-acyclic triangulation. |
We present a 4-dimensional polyhedral realization of a 2-dimensional Z-acyclic but non-contractible simplicial complex with 23 vertices.
Our example answers a query by Lutz Hille (Hamburg), who in November 2006 had asked us for examples of Z-acyclic but non-contractible complexes realized in low dimensions. His question was motivated by toric geometry. Indeed, any 2-dimensional complex with rational coordinates in R4 corresponds to a subfan of a complete fan in R5, which in turn determines a 5-dimensional toric variety. Cohomology computations for line bundles on the toric variety, as considered in [1, 7, 8], can be reduced to cohomology computations for closed subcomplexes, as provided here. In this context, the question for the difference between homological triviality (acyclicity) and homotopical triviality (contractibility) arises naturally.
Our model demonstrates explicitly that for 2-dimensional complexes piecewise linearly (PL) embedded in R4 homotopy conditions are stronger than homological ones. The respective dimensions hereby are smallest possible: Z-acyclic but non-contractible 2-dimensional complexes do not have PL embeddings in R3, whereas all 1-dimensional (finite) Z-acyclic complexes are contractible.
A famous example of a Z-acyclic but non-contractible complex is due to Floyd and Richardson [4]: Let SO(3) be the group of 3-dimensional rotations and I be the subgroup of rotational symmetries of the icosahedron. The group I is isomorphic to the alternating group A5 and acts on the coset space SO(3)/I, which is homeomorphic to the Poincaré homology 3-sphere; cf. [10]. By removing the open star of the point I from (an appropriate cell decomposition of) the quotient SO(3)/I, we obtain a 2-dimensional (cellular) complex K that is Z-acyclic but non-contractible and on which I acts freely. Alternatively, the complex K arises as the 2-skeleton of the Poincaré homology 3-sphere in its description by Weber and Seifert [17] as the spherical dodecahedral space. The complex K has the binary icosahedral group I* as its fundamental group.
In fact, every homology 3-sphere Σ3 different from S3 can be used to yield a Z-acyclic but non-contractible 2-dimensional complex. One way to describe any such Σ3 is as a 3-dimensional (polyhedral) ball with identifications on the boundary (cf. Seifert [16]). As in the Floyd-Richardson example, the identified boundary is a Z-acyclic but non-contractible 2-dimensional complex.
Newman [15] gave yet another construction of a Z-acyclic complex (non-homeomorphic to the complex K above, but also with fundamental group I*) by identifying the boundaries of two circular discs. Wedges as well as connected sums of Z-acyclic complexes are Z-acyclic again and thus yield further examples.
All finite 1-dimensional Z-acyclic complexes are trees and hence are contractible. As planar graphs, they are geometrically realizable in R2.
The embedding respectively the PL embedding of 2-dimensional Z-acylic complexes is a more delicate matter. As pointed out by Zeeman [19], there are contractible 2-dimensional simplicial complexes that cannot be embedded (topologically) in any 3-manifold, for example, cones over non-planar graphs. However, any (finite) 2-complex is embeddable in some 4-manifold and every contractible 2-complex can be embedded in R4; see Curtis [2]. (As remarked in [12], it is not known whether all contractible 2-dimensional complexes have a PL embedding in R4.) Such embeddings can be complicated (Curtis, cf. [5]): there is an embedding of a 2-dimensional contractible complex L in S4 such that the complement S4\L is not simply connected. Note that in this situation Alexander duality implies that S4\L is Z-acyclic. For further embeddings with non-simply connected complement see Glaser [5, 6] and Neuzil [14].
It was later proved by Kranjc [11; Cor. 2 and Rem. 2] that arbitrary finite Z-acylic 2-dimensional complexes are topologically embeddable in R4. A class of polyhedral homology 3-spheres in R4 with non-trivial fundamental group was given by Curtis and Wilder [3]. These yield examples of PL embeddings of non-contractible Z-acylic 2-dimensional complexes in R4. In the following, we present a model with few vertices.
Theorem: There is a 2-dimensional Z-acyclic but non-contractible simplicial complex on 23 vertices that has a polyhedral realization (with small integer coordinates) in R4.
Proof: We appropriately subdivide the 2-skeleton of the spherical dodecahedral space (see above and cf. [13]) to obtain a Z-acyclic but non-contractible 2-dimensional simplicial complex with 23 vertices, A, B,...,W; see Figure 3 for the respective triangulation. We then remove the star of the vertex A from the triangulation to obtain the shaded complex of Figure 3. A 3-dimensional geometric realization of this shaded complex is visualized in Figure 1. Finally, the star of vertex A is added by placing this vertex in R4 at position (0,0,0,1). To be more precise: The vertices B, C, D, and E of the shaded complex are connected to each other. They form the complete graph K4 which is the 1-skeleton of the tetrahedron. Each of the six original pentagons of the 2-skeleton of the spherical dodecahedral space is subdivided (in a symmetric way) by inserting three additional vertices each. For example, the pentagon A-B-C-D-E is subdivided by adding the vertices F, G, and H. In each of the six pentagons there is a strip of five shaded triangles which is glued to the tetrahedral graph formed by the vertices B, C, D, and E. Each of the stripes is colored in a different color. It can be inspected in the applet how the stripes wind arround the tetrahedral graph. The coordinates of the realization are chosen such that the rotation group of the tetrahedron acts on the model. All the coordinate entries that occur in the model are integers between -4 and +4.
The 3-dimensional realization of the shaded complex cannot be extended to a 3-dimensional realization of the full complex since the link of vertex A is linked in the realization (see Figure 2).
In fact, 2-dimensional Z-acyclic but non-contractible simplicial complexes never have PL embeddings in R3: Suppose, there is such a PL embedding. Any regular neighborhood (cf. [18]) of the embedded complex yields a Z-acyclic 3-manifold with S2 as boundary (cf. [9, p. 114]). However, by the Schoenflies theorem, S2 bounds a 3-ball with trivial fundamental group, contradiction.
Acknowledgement: The authors were supported by the DFG Research Group "Polyhedral Surfaces", Berlin.
| Keywords | Z-acyclic and contractible complexes; polyhedral realizations | |
| MSC-2000 Classification | 52B99 (57Q15, 51M20) | |
| Zentralblatt No. | 05613404 |
Submitted: Wed May 30 09:47:38 CEST 2007.
Revised: Fri Nov 21 15:05:31 CET 2008.
Accepted: Mo Nov 24 15:28:50 CET 2008.
Technische Universität BerlinGünter M. Ziegler
Institut für Mathematik, MA 3-2
10623 Berlin
Germany
lutz@math.tu-berlin.de
http://www.math.tu-berlin.de/~lutz
Technische Universität Berlin
Institut für Mathematik, MA 6-2
10623 Berlin
Germany
ziegler@math.tu-berlin.de
http://www.math.tu-berlin.de/~ziegler